Types of PPF & Their Pros and Cons
Polyethylene (PE or TPH) PPF
- Pros:
- Cheapest type of PPF
- Easy to install
- High transparency
- Cons:


Polyurethane (PU) PPF
Pros:
- Thicker
- More resistant to deep scratches
- Longer lifespan
- Self-healing
Cons:
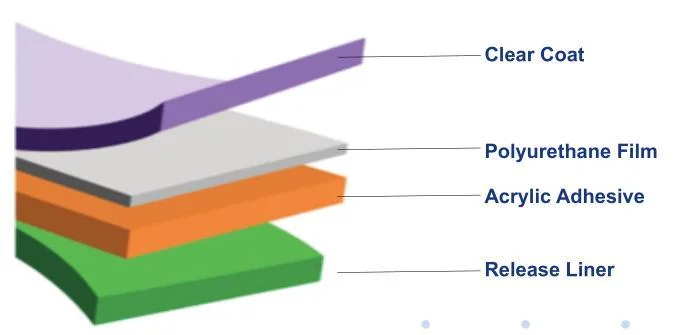

Vinyl (PVC) PPF
Pros:
- Inexpensive
- Easy to install
- UV resistant
Cons:
- Low thickness
- Low scratch resistance
- Short lifespan


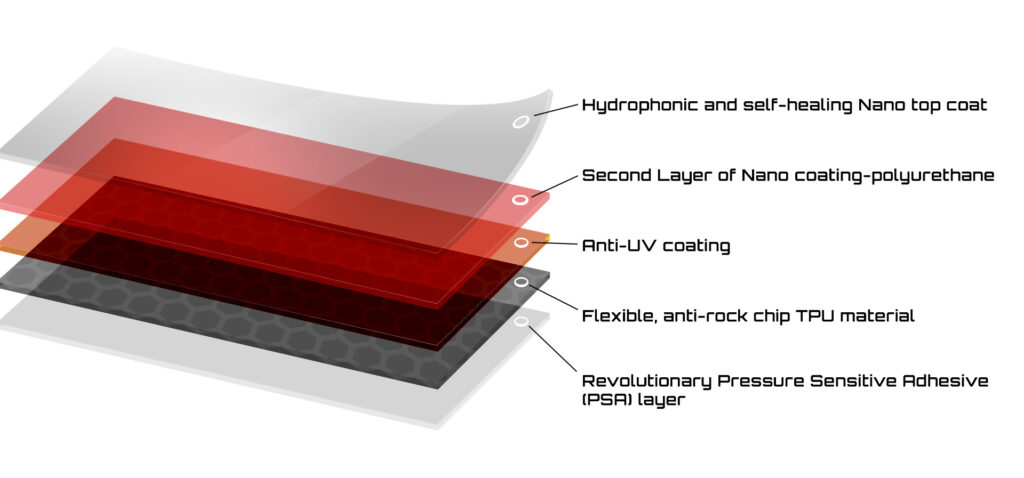
TPU PPF (Hybrid)
Pros:
- Combines the advantages of polyethylene, polyurethane, and vinyl PPFs
- Typically thicker and more durable than single-material PPFs
- Self-healing
Cons:
- Most expensive type of PPF
- More difficult to install

Factors to Consider When Choosing a PPF
- Budget: PPFs are available in a wide range of prices. Before you buy, determine your budget and choose a PPF that fits your price range.
- Your Needs: Think about what kind of protection you need. If you live in an area with harsh weather conditions, you need a PPF that is resistant to UV rays and chemicals. If you are concerned about deep scratches, you need a thicker PPF.
- Appearance: PPFs are available in a variety of transparency levels. If you want to preserve the appearance of your car’s paint, choose a PPF that is completely transparent.
PPF Installation
PPF should be installed by a qualified installer. Improper installation can lead to bubbles, wrinkles, and other problems.
Cost of PPF Installation
The cost of PPF installation depends on various factors, including the size of the vehicle, the type of PPF, and the installation location. In general, you can expect to pay between $500 and $2000 for PPF installation.
Benefits of Using PPF
- Protects paint from scratches, chips, impacts, and gravel: PPF can protect your car’s paint from various damages.
- Protects paint from UV rays: PPF can protect your car’s paint from fading and discoloration caused by UV rays.
- Increases car value: PPF can help maintain the value of your car.
- Easy to clean: PPF can make it easier to clean your car.
Drawbacks of Using PPF:
- Cost: PPF can be expensive, especially if you have it installed by a professional installer.
- Appearance: Some PPFs may be slightly matte.
- Difficulty in removal: PPF can be difficult to remove, especially if it has been on the car for a long time.
Distinguishing TPU from TPH
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane) and TPH (Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer) are both types of thermoplastic elastomers (TPEs) that are commonly used in a variety of applications, including automotive, construction, and consumer products. However, there are some key differences between the two materials that can affect their performance and suitability for specific applications.
TPU (Thermoplastic Polyurethane)
TPU is a versatile material that is known for its excellent combination of strength, flexibility, and durability. It is also resistant to abrasion, chemicals, and UV rays. TPU is often used in applications where these properties are important, such as:
- Automotive: TPU is used in a variety of automotive components, such as bumpers, fenders, and seat covers.
- Construction: TPU is used in roofing membranes, waterproofing membranes, and expansion joints.
- Consumer products: TPU is used in footwear, hoses, and cables.
TPH (Thermoplastic Polyester Elastomer)
TPH is another type of TPE that is known for its soft, flexible texture and good chemical resistance. It is also less expensive than TPU. TPH is often used in applications where these properties are important, such as:
- Medical: TPH is used in medical devices, such as catheters and tubing.
- Consumer products: TPH is used in toys, sporting goods, and apparel.
Key Differences Between TPU and TPH
Here is a table summarizing the key differences between TPU and TPH:
| Feature | TPU | TPH |
|---|---|---|
| Strength | Higher | Lower |
| Flexibility | Moderate | Higher |
| Abrasion resistance | Higher | Lower |
| Chemical resistance | High | Good |
| UV resistance | High | Moderate |
| Temperature resistance | Wide range | Narrower range |
| Cost | More expensive | Less expensive |
Choosing Between TPU and TPH
The best material for a specific application will depend on the specific requirements of the application. Here are some factors to consider when choosing between TPU and TPH:
- Strength: If the material needs to be strong enough to withstand high impact or stress, TPU is a better choice.
- Flexibility: If the material needs to be flexible and easy to bend, TPH is a better choice.
- Abrasion resistance: If the material will be exposed to wear and tear, TPU is a better choice.
- Chemical resistance: If the material will be exposed to chemicals, both TPU and TPH are good choices.
- UV resistance: If the material will be exposed to UV rays, TPU is a better choice.
- Temperature resistance: If the material needs to be able to withstand extreme temperatures, TPU is a better choice.
- Cost: If cost is a major concern, TPH is a more affordable option.
One of the appearance tests


